Quarkus Security architecture
The Quarkus Security architecture provides several built-in authentication mechanisms and is highly customizable.
The primary mechanism for securing HTTP applications in Quarkus is the HttpAuthenticationMechanism interface.
Overview of the Quarkus Security architecture
When a client sends a HTTP request, Quarkus Security orchestrates security authentication and authorization by interacting with several built-in core components, including HttpAuthenticationMechanism, IdentityProvider, and SecurityIdentityAugmentor.
The sequential security validation process results in one of three outcomes:
-
The HTTP request gets authenticated and authorized, and access to the Quarkus application gets granted.
-
The HTTP request authentication fails, and the requester receives a challenge specific to the authentication mechanism, for example, a
401error, a URL redirect to reauthenticate, or some other custom authentication challenge response. For practical examples of challenge responses, see the Quarkus Security Tips and Tricks guide. -
The HTTP request authorization fails, and the requester gets denied access to the Quarkus application.
The following diagram steps through the detailed process flow of the Quarkus Security architecture:
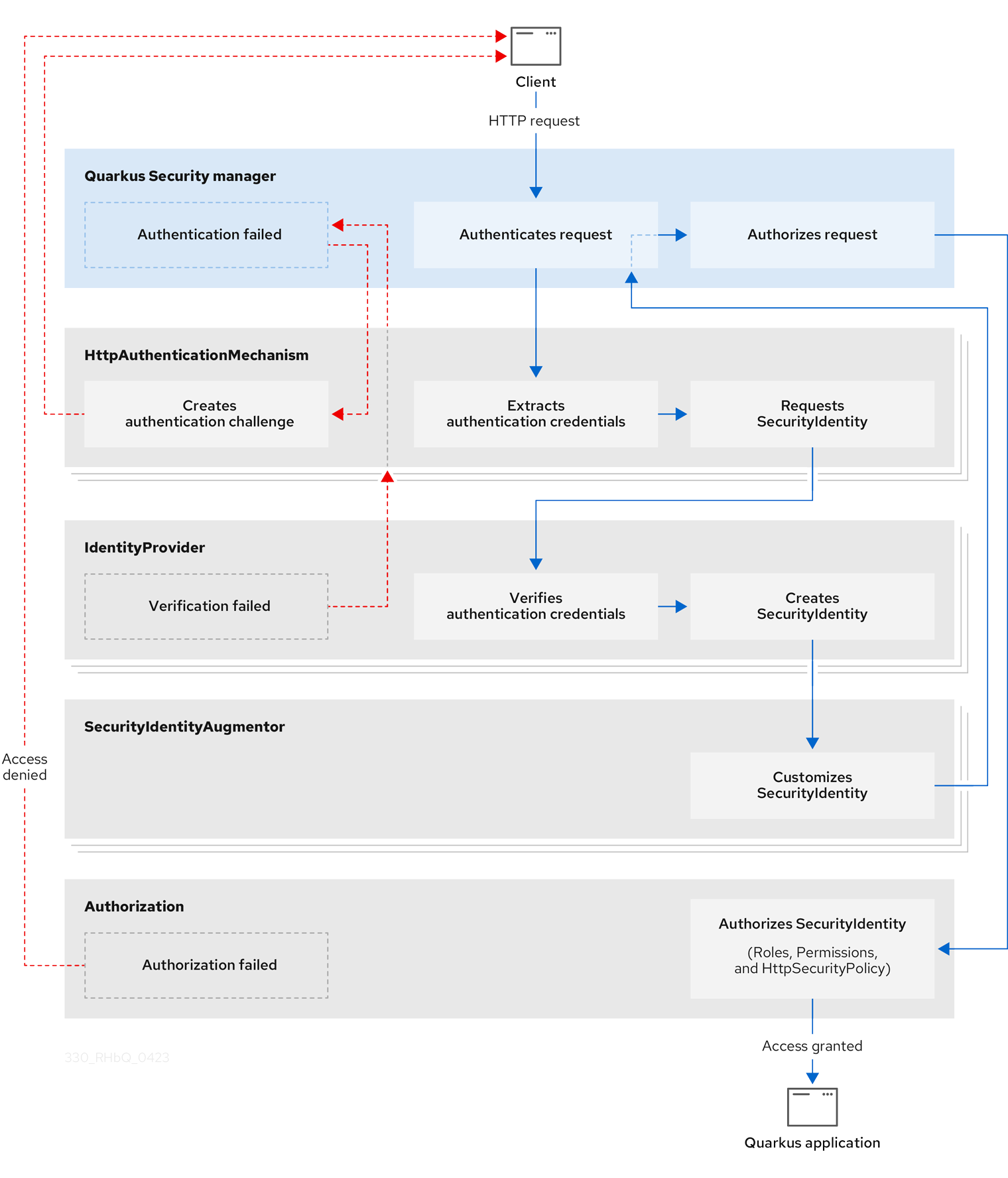
Core components of the Quarkus Security architecture
HttpAuthenticationMechanism
Quarkus Security uses HttpAuthenticationMechanism to extract the authentication credentials from the HTTP request and delegates them to IdentityProvider to convert the credentials to SecurityIdentity.
For example, the credentials can come from the Authorization header, client HTTPS certificates, or cookies.
When Quarkus Security rejects an authentication request, HttpAuthenticationMechanism returns an authentication challenge to the client.
The type of challenge depends on the authentication mechanism.
For example, with the OIDC OpenID Connect (OIDC) Authorization Code Flow mechanism, a redirect URL gets generated, and the client is returned to the OpenID Connect provider to authenticate.
IdentityProvider
IdentityProvider verifies the authentication credentials and maps them to SecurityIdentity, which has the username, roles, original authentication credentials, and other attributes.
You can inject a SecurityIdentity instance for every authenticated resource to get the authenticated identity information.
In other contexts, it is possible to have other parallel representations of the same information or parts of it, for example, SecurityContext for Jakarta REST or JsonWebToken for JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
For more information, see the Quarkus Identity providers guide.
SecurityIdentityAugmentor
Because Quarkus Security is customizable, you can, for example, add authorization roles to SecurityIdentity and register and prioritize one or more SecurityAugmentor implementations.
Registered instances of SecurityIdentityAugmentor are invoked during the final stage of the security authentication process.
For more information, see the Security Identity Customization section of the "Security Tips and Tricks" guide.
Supported authentication mechanisms
The Quarkus Security framework supports multiple authentication mechanisms, which can also be combined. Some supported authentication mechanisms are built into Quarkus, while others require you to add an extension.
To learn about security authentication in Quarkus and the supported mechanisms and protocols, see the Quarkus Authentication mechanisms in Quarkus guide.
Proactive authentication
Proactive authentication is enabled in Quarkus by default. The request is always authenticated if an incoming request has a credential, even if the target page does not require authentication. For more information, see the Quarkus Proactive authentication guide.
Quarkus Security customization
Quarkus Security is customizable. You can customize the following core security components of Quarkus:
-
HttpAuthenticationMechanism -
IdentityProvider -
SecurityidentityAugmentor
For more information about customizing Quarkus Security, including reactive security and how to register a security provider, see the Quarkus Security tips and tricks guide.
