Dev MCP
|
Experimental
This feature is currently experimental. |
Overview
When you run a Quarkus application in dev mode, you can expose a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server. It presents the methods used by the DevUI MCP tools (methods you can call) and the data exposed by MCP resources.
Connecting an MCP client
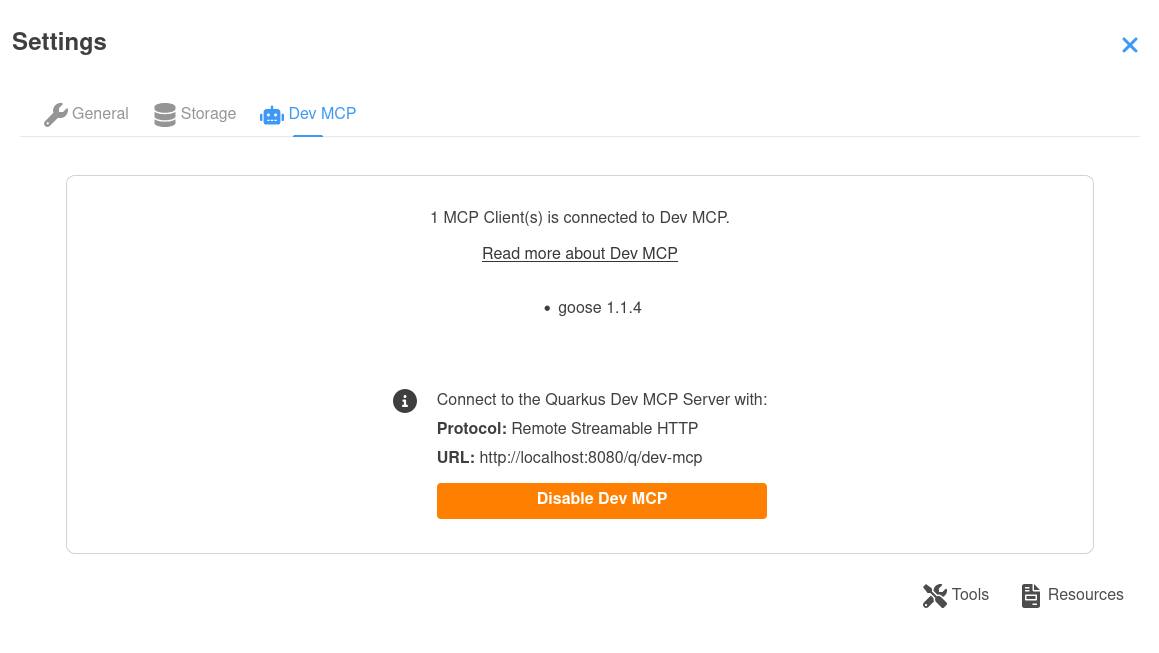
Open the Dev UI settings dialog and select the Dev MCP tab.
There you can enable Dev MCP, get the connection details (Default http://localhost:8080/q/dev-mcp) and see what clients are connected.
Any MCP client that supports the Streamable Protocol, version 2025‑03‑26 can connect using that URL. After a client connects, it will appears on the tab:
Guide for extension developers
Extensions can contribute additional tools and resources to the Dev MCP server. The integration is similar to contributing to the Dev UI, but descriptions are mandatory. A single JSON‑RPC service can be used for both Dev UI and Dev MCP; methods without a description only show up in Dev UI, while methods with a description appear in both.
MCP resources
A resource is data exposed by your extension. There are two ways to create a resource.
MCP Resources against build time data
Build‑time data that is already exposed to the Dev UI can also be made available to Dev MCP. Provide a description when calling addBuildTimeData():
footerPageBuildItem.addBuildTimeData(
"jokes",
jokesBuildItem.getJokes(),
"Some funny jokes that the user might enjoy"
);The extra description argument is new: without it the data only appears in the Dev UI. Once supplied, the jokes data becomes an MCP resource, however, by default this resource will be disabled. You can change the default by passing in true as another parameter after description, that will change this default to be enabled. Users can change this in Dev UI anyway, so this is just a sensible default.
footerPageBuildItem.addBuildTimeData(
"jokes",
jokesBuildItem.getJokes(),
"Some funny jokes that the user might enjoy",
true
);MCP Resources against a recorded value
To expose recorded values (data produced at runtime by a recorder) as an MCP resource, define a build‑time action in the deployment module. The action must include a description:
@BuildStep(onlyIf = IsLocalDevelopment.class)
BuildTimeActionBuildItem createBuildTimeActions() {
BuildTimeActionBuildItem item = new BuildTimeActionBuildItem(); (1)
item.actionBuilder() (2)
.methodName("getMyRecordedValue")
.description("A well‑thought‑out description") (3)
.runtime(runtimeValue) (4)
.build();
return item;
}| 1 | Return or produce a BuildTimeActionBuildItem. |
| 2 | Use the builder to configure the action. |
| 3 | Set a human‑readable description. |
| 4 | Provide the runtime value returned by your recorder. |
By default this resource will be disabled, and the user has to enable it in Dev UI. You can change this default by adding .enableMcpFuctionByDefault() in the builder method.
MCP tools
A tool corresponds to a method that a client can call. Any JSON‑RPC method can be exposed as a tool by supplying descriptions on the method and its parameters. Tools can run on either the runtime or deployment classpath.
MCP Tools against the Runtime classpath
To expose runtime information or actions (for example, changing log levels), define a JSON‑RPC service in your runtime or runtime‑dev module and annotate the methods and parameters with @JsonRpcDescription:
public class MyExtensionRPCService {
@JsonRpcDescription("Update a specific logger's level in this Quarkus application") (1)
public JsonObject updateLogLevel(
@JsonRpcDescription("The logger name as defined in the logging implementation") String loggerName,
@JsonRpcDescription("The new log level") String levelValue) { (2)
// implementation…
}
}| 1 | Description of the method. |
| 2 | Description of each parameter. |
By default this tool will be disabled, and the user has to enable it in Dev UI. You can change this default by adding the @DevMCPEnableByDefault annotation on the method.
You must register the JSON‑RPC service in the deployment module:
@BuildStep
JsonRPCProvidersBuildItem registerRpcService() { (1)
return new JsonRPCProvidersBuildItem(MyExtensionRPCService.class); (2)
}| 1 | Produce a JsonRPCProvidersBuildItem. |
| 2 | Specify the class in your runtime or runtime‑dev module that contains the methods. |
@JsonRpcDescription is mandatory for Dev MCP; without it the method is only available in the Dev UI.
The method can return primitives, String, JsonObject, JsonArray, or any POJO that can be serialised to JSON.
Asynchronous methods (Uni, CompletionStage or methods annotated with @NonBlocking) are also supported.
MCP Tools against the Deployment classpath
Sometimes you need to run actions on the deployment classpath (for example, writing configuration files). In that case you do not create a JSON‑RPC service; instead you provide a supplier via a BuildTimeActionBuildItem:
@BuildStep(onlyIf = IsLocalDevelopment.class)
BuildTimeActionBuildItem createBuildTimeActions() {
BuildTimeActionBuildItem actions = new BuildTimeActionBuildItem();
actions.actionBuilder()
.methodName("updateProperty")
.description("Update a configuration/property in the Quarkus application") (1)
.parameter("name", "The name of the configuration/property to update") (2)
.parameter("value", "The new value for the configuration/property")
.function(map -> {
Map<String, String> values = Collections.singletonMap(
map.get("name"), map.get("value"));
updateConfig(values);
return true;
})
.build();
return actions;
}| 1 | Description of the method. |
| 2 | Description of each parameter. |
The code in the function runs on the deployment classpath. The function can return a plain value, a CompletionStage or CompletableFuture for asynchronous work.
By default this tool will be disabled, and the user has to enable it in Dev UI. You can change this default by adding .enableMcpFuctionByDefault() in the builder method.
